Varicella vaccine
This is a practical guide to Varicella vaccination.
The best part?
We’ll give you only factual information based on reliable sources and our nearly 20 years of experience in travel medicine.
Contents
At a glance
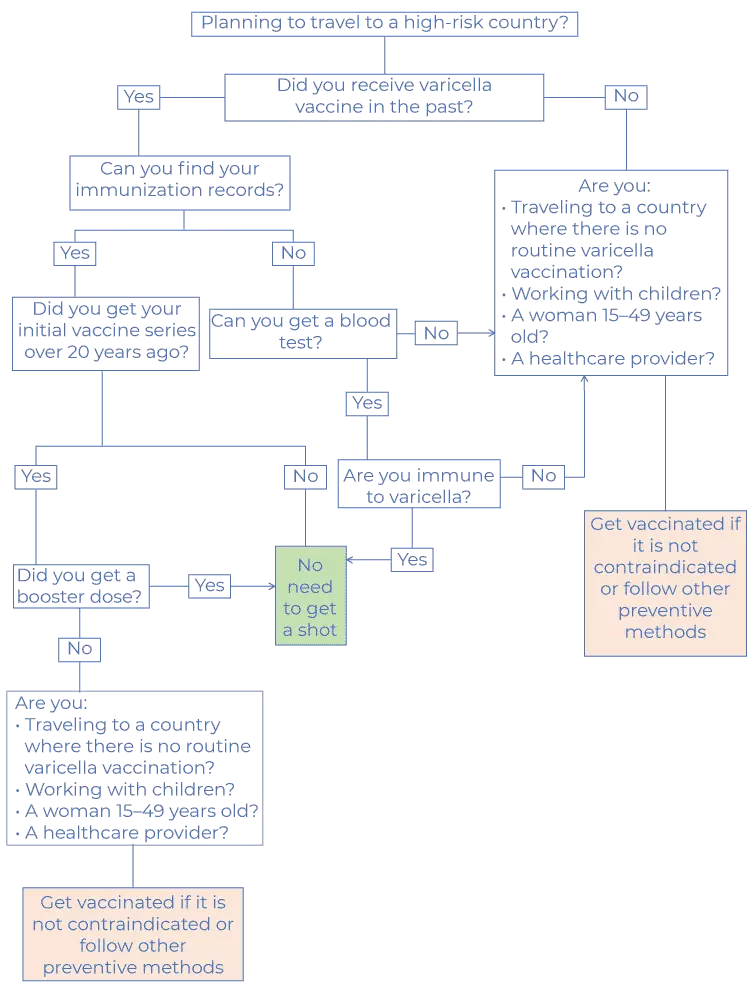
 Required or recommended? The centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends it; no countries require it
Required or recommended? The centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends it; no countries require it How is varicella transmitted? Via contact with an infected person (see the details below)
How is varicella transmitted? Via contact with an infected person (see the details below) Is varicella vaccine a part of routine childhood immunizations? Yes; two doses of the varicella vaccine are given to children as a part of routine childhood immunizations
Is varicella vaccine a part of routine childhood immunizations? Yes; two doses of the varicella vaccine are given to children as a part of routine childhood immunizations Duration of varicella vaccine protection: 10-20 years
Duration of varicella vaccine protection: 10-20 years Is an adult booster necessary? Yes! a booster dose of varicella vaccine is necessary for those who have no proof of immunity to chickenpox
Is an adult booster necessary? Yes! a booster dose of varicella vaccine is necessary for those who have no proof of immunity to chickenpox
Varicella Vaccine Info
Childhood vaccine schedule
The table below shows the varicella (chickenpox) childhood immunization schedule. Please, check your records to see whether you have received all the shots at the recommended time intervals.
First dose at 12–15 months of age
Second dose at 4–6 years of age
Single dose: 85%
Two doses: 98%
Varicella Vaccine Protection
Single dose: 10 years
Two doses: Up to 20 years
Adult booster schedule
The table below shows the recommended vaccination schedule for adults who completed their varicella childhood immunization.
Those who do not have proof of chickenpox immunity need two shots of of chickenpox vaccine four to eight weeks apart.
If a person has been previously vaccinated (or has a decreased level of immunity to varicella) and it has been more than eight weeks since his or her varicella (chickenpox) shot, only one booster dose will be needed.
These shots are especially needed for the following:
International travelers
Healthcare providers
Women of reproductive age (ages 15–49)
People with children in their family
School personnel
Military personnel
Up to 98%
Varicella Booster Vaccine Protection
Up to 20 years

Where Is Varicella Most Common
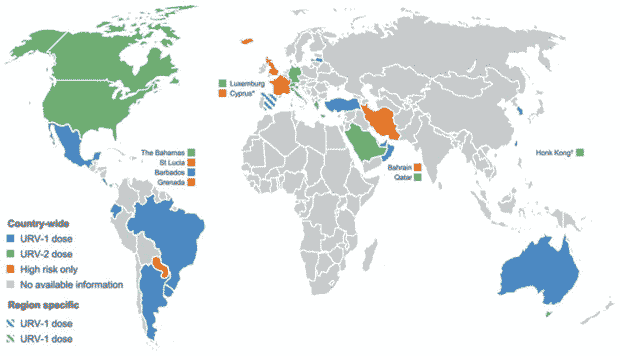
Varicella or chickenpox [1] Varicella / Chickenpox https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2024/infections-diseases/varicella-chickenpox is primarily a pediatric infection that affects millions of people worldwide. It is highly contagious and is caused by a varicella-zoster virus. Each year, this disease causes about 4.2 million life-threatening complications and over 4,000 deaths. The disease has spread worldwide and it is difficult to determine if there are areas that are more affected than others. The outbreaks of the disease cause serious public health problems. However, routine administration of varicella vaccine decreases the number of cases by up to 90%. So, we can assume that countries that do not have varicella vaccination in their national immunization program are more commonly affected than others. The map below shows the countries that are practicing routine varicella vaccination.

About Varicella Infection
Varicella is a viral infection that mainly affects children. When adults and adolescents do get it, they have an up-to-50-times-higher chance of having a severe form of the disease and a 174-times-higher chance of death. This section summarizes the most important facts about varicella.

Varicella Vaccination FAQ
Here are the questions our patients frequently ask about the Varicella vaccination.
[2]
Chickenpox/Varicella Vaccination
https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd/varicella/index.html
We’ve answered them based on 20 years of being the busiest walk-in travel clinic in Midtown Manhattan.
Let’s dive in!